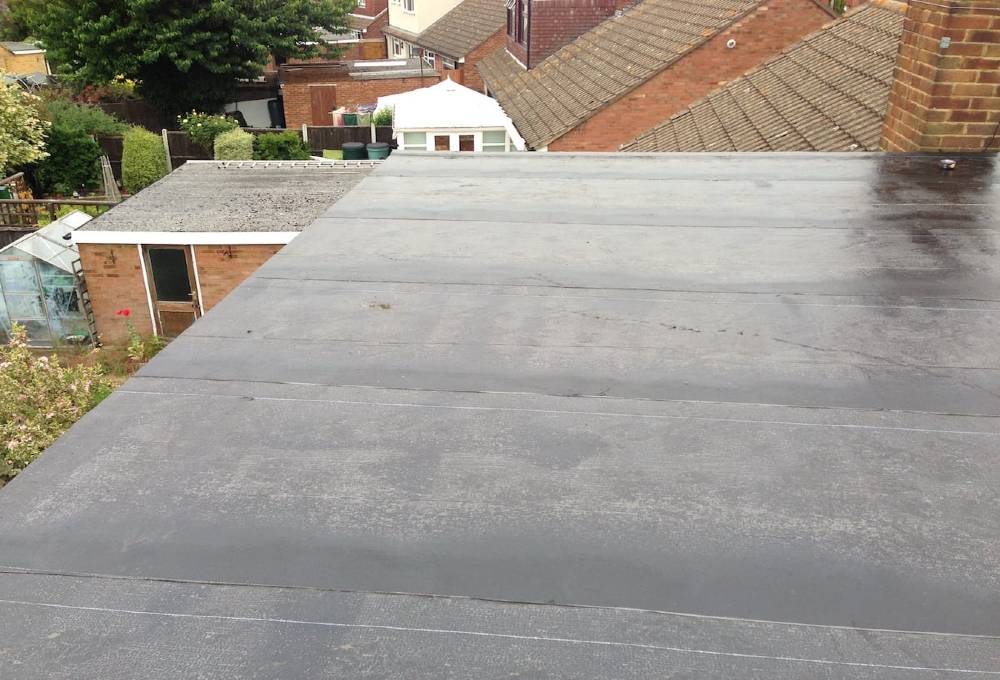
Roofing felt is comprised of a base made from natural materials such as wood cellulose or synthetic ones such as fiberglass or polyester and then coated or saturated with a protective coating such as bitumen asphalt which repels water but still allows the product to breathe.
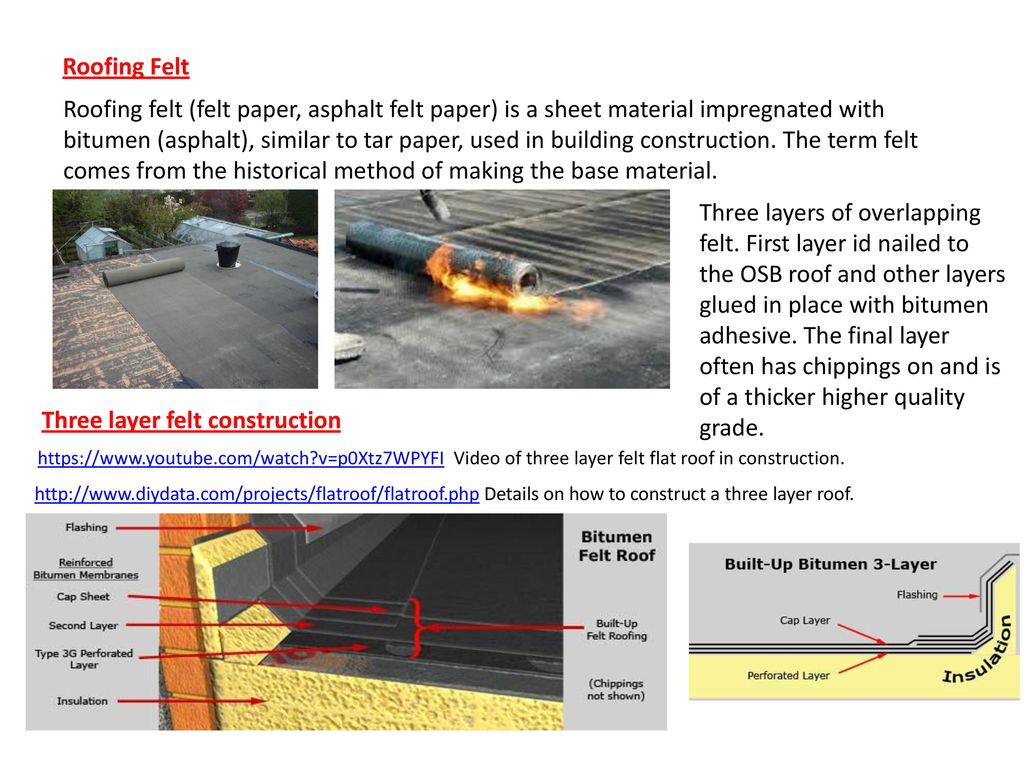
Three layer felt roofing method.
Laying roofing felt this is then applied to a fibrous membrane which is typically made of fibreglass polyester or hessian.
Traditional roll and pour three layer.
Another method for fixing low spots is to apply new roofing plies to the problem spot.
The two main methods of its application are pour roll and torch on.
This layer is not bonded to the decking so that the decking can move without damaging the felt roof.
Old style flat roofs were often designed with pieces of asphalt felt paper sandwiched between tar.
These layers are all laid in a half lap manner so all the joints are the furthest away they can be from another joint.
Typically it s applied as a 3 layer system usually consisting of a perforated underlay a 2mm underlay layer then thick 4 5mm felt.
Each of the three layers is laid in a half lap system so any joint in the roof is as far away as possible from another joint.
They are no longer laid with hot bitumen and have stone chippings put on top.
Laying the first nailed layer of underlay felt.
Showing the method of roll and pour on fixing felt onto a flat roof.
The products used today are a 3 layer membrane system applied with the use of a gas gun.
Fitted using a blowtorch the 3 layer felt roof system benefits from being more stable than the older methods.
The 3 layer felt roof system is also versatile when it comes to appearance.
Laying the second bonded layer of underlay felt.
An extra coating of sand or fine gravel can be added on top to improve the aesthetic appeal.
In these kinds of felt roofs it is possible to fill low spots with two or three layers of felt applied with tar or another bitumen.
Installing any gutter drips.
Showing the method of roll and pour on fixing felt onto a flat roof.